Environment settings
Environment Settings
Gimlet is a Bring Your Own Hardware platform. Each environment is deployed on its own Kubernetes cluster.
If you don't know how to launch a cluster, check out providers like civo.com where you can have a useful cluster for $20 a month, with swift setup experience. Or you can launch a cluster on your laptop with k3d as described on our blog.
If you use our cloud environment an ephemeral cluster is provided for 7 days so you don't need to deal with Kubernetes clusters when you start. Just skip ahead to deployment.
There is a possibility to map environments to Kubernetes namespaces, thus hosting multiple environments on the same cluster.
Gimlet also works well on vcluster.
Join our Discord to learn more.
Environment Settings
Gimlet aids cluster setup with preconfigured stacks. With a marketplace-like experience you can configure common usecases:
- SSL certificates
- Custom domain names
- Metrics and dashboards
- Secrets
Gitops Repositories
Gimlet is not writing Kubernetes directly during component settings changes. Gimlet writes all manifests to git, then the Flux project syncronizes the git state to Kubernetes. This has the added benefit of having all your configuration in code.
By convention, we maintain two git repositories per environment:
- one for application deployments:
gitops-<env>-apps - one for infrastructure components:
gitops-<env>-infra
Repository Structure
The gitops-<env>-infra repository follows the following convention
dependenciesare synced first to the clusterhelm-repositoriesandhelm-releaseshold content accordinglymanifestsis a catch-all for everything elsestack.yamlholds metadata about the environment
$ tree gitops-optimal-snow-infra
├── README.md
├── dependencies
│ └── namespace.yaml
├── flux
│ ├── deploy-key-laszlocph-gitops-optimal-snow-infra.yaml
│ ├── flux.yaml
│ └── gitops-repo-builtin-infra.yaml
├── helm-releases
│ ├── gimlet-agent.yaml
│ ├── image-builder.yaml
│ └── sealed-secrets.yaml
├── helm-repositories
│ ├── onechart.yaml
│ └── sealed-secrets.yaml
├── manifests
│ ├── capacitor.yaml
│ ├── customregistry-registrycert.yaml
│ ├── customregistry-secret.yaml
│ ├── docker-registry.yaml
│ ├── dockerhubregistry-secret.yaml
│ ├── ghcrregistry-secret.yaml
│ └── oauth2-proxy.yaml
└── stack.yaml
Editing Environment Settings
Navigate to the Environments page in the top menu, then pick the environment card you want to edit.
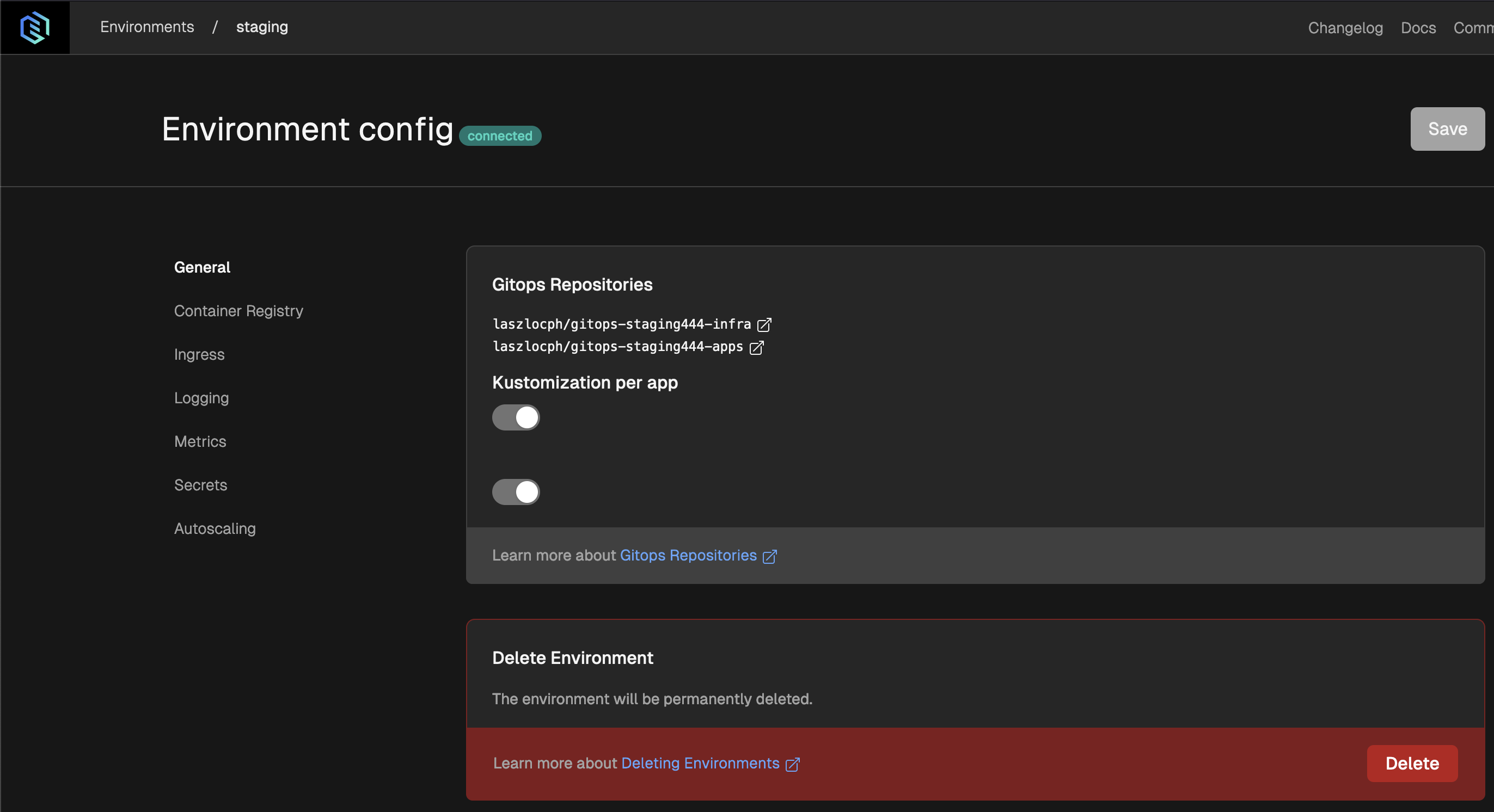
Locate and edit the components in the side menu then hit Save and inspect the gitops commit Gimlet makes in your infrastructure configuration gitops repository.
You can monitor the components as they come up by toggling the gitops view in the footer of Gimlet.
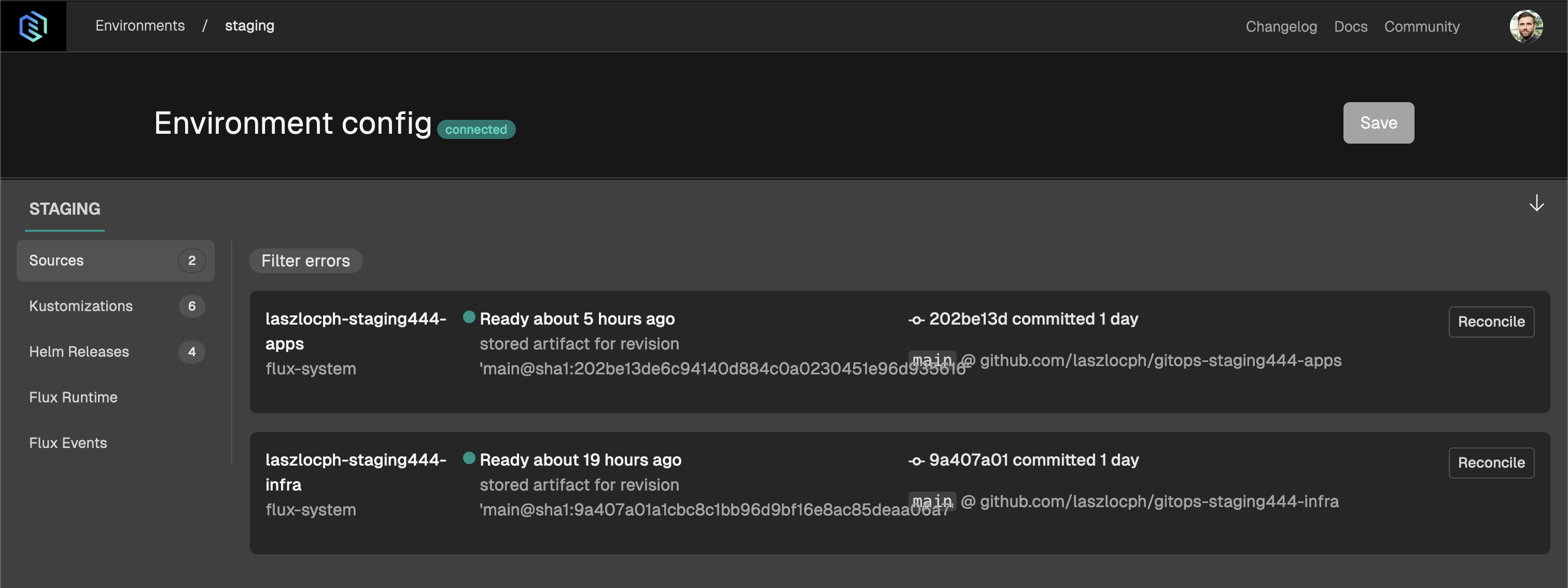
Inspecting the Differences
Before you save the configuration on the dashboard, you can inspect the differences that will be saved to your infrastructure gitops repository. Click Review changes to see the changes in yaml format.
In Your Editor
You can also change the files in your editor. Gimlet handles the changes quite well, and even preserves your custom changes throughout component updates.
Also, feel free to add new files to this repository, HelmReleases or just plan Kubernetes manifests that are needed in your environment.