Resource widget and cluster management

Laszlo Fogas
This week's update is about resource management.
Learn about the new CPU/Memory widgets and how you can configure them appropriately to keep cluster resources in check.
Resource widget
Developers want to be good citizens. If they have all the knowledge required to set requests and limits correctly, they do it.
Trainings, wikis, enforcement, feedback loops all suffer from a key problem however. They are not helping when developers have the most attention on the problem. When they are setting requests and limits.
Often they are on a mission to deploy their application, and the configuration details are just obstacles to reach that goal. Setting just some value is often their approach to get through this hurdle.
In Gimlet, we build the knowledge right in the tooling. Developers have the hints right where they need it, when they focus on the problem.
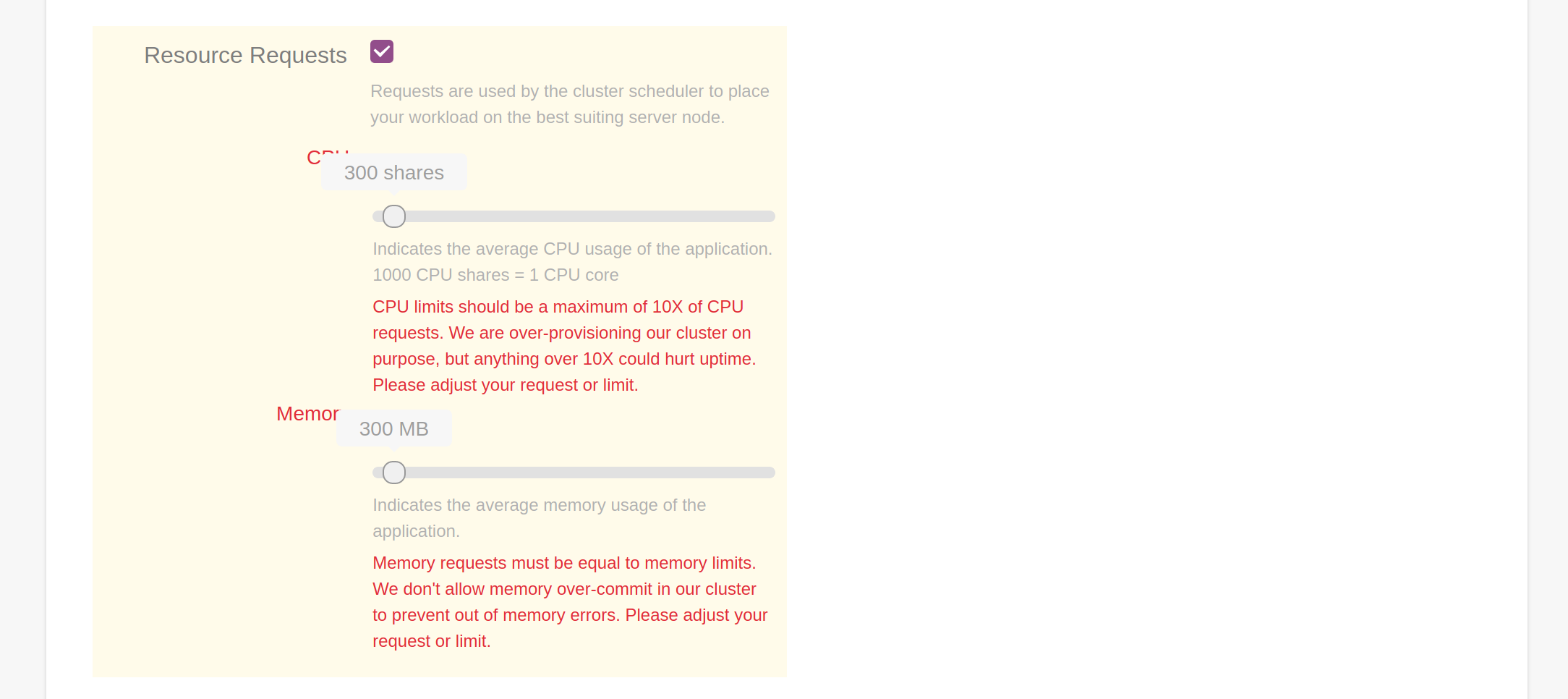
Customizing the resource boundaries
All application configuration options are coming from the Master Template.
For the resource widget, we introduced a new variable type in the questions.yaml file.
Please meet the int variables with range:
questions:
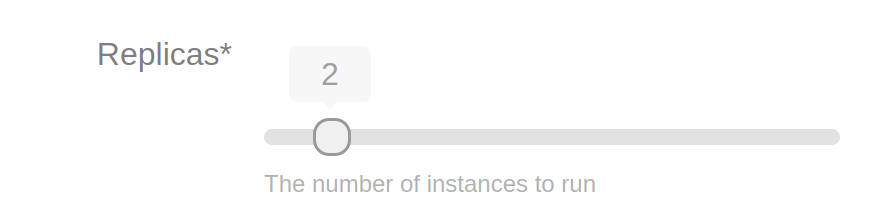
- variable: replicas
label: Replicas
description: The number of instances to run
type: int
group: misc
required: true
default: 1
range:
min: 1
max: 12
step: 1
They accept two new validation strategies as well: minRatio and maxRatio:
questions:
- variable: requests
label: Resource Requests
description: "Requests are used by the cluster scheduler to place your workload on the best suiting server node."
type: complex
required: false
group: resources
patch: resourceRequests.yaml
subquestions:
- variable: cpu
label: CPU
description: "Indicates the average CPU usage of the application. 1000 CPU shares = 1 CPU core"
type: int
default: 500
range:
min: 100
max: 8000
step: 100
unit: "m"
readableUnit: "shares"
+ validation:
+ - type: minRatio
+ variable: limits.cpu
+ value: 0.1
+ description: "CPU limits should be a maximum of 10X of CPU requests. We are over-provisioning our cluster on purpose, but anything over 10X could hurt uptime. Please adjust your request or limit."
Learn more about the Master Template in the documentation.
Over-committing cluster resources using min and maxRatio
As a cluster administrator you want to be in control of cluster resources. Over-comitting can save money, but extensive over-committing can cause issues down the line.
With minRatio and maxRatio you can keep over-committing in a desired range.
Edit the Master Template to reflect your policies.
Conservative CPU over-commit
This example follows a more moderate over-commit approach. Allows to burst each resource to use 5X of its budgeted CPU.
questions:
- variable: requests
label: Resource Requests
description: "Requests are used by the cluster scheduler to place your workload on the best suiting server node."
type: complex
required: false
group: resources
patch: resourceRequests.yaml
subquestions:
- variable: cpu
label: CPU
description: "Indicates the average CPU usage of the application. 1000 CPU shares = 1 CPU core"
type: int
default: 500
range:
min: 100
max: 8000
step: 100
unit: "m"
readableUnit: "shares"
validation:
- type: minRatio
variable: limits.cpu
- value: 0.1
+ value: 0.2
description: "CPU limits should be a maximum of 10X of CPU requests. We are over-provisioning our cluster on purpose, but anything over 10X could hurt uptime. Please adjust your request or limit."
Strict memory management
This example does not allow any memory over-commit.
While CPU over-commit only slows things down should all workload burst at the same time. Memory over-commit starts evicting pods, which may cause downtime of workloads.
questions:
- variable: requests
label: Resource Requests
description: 'Requests are used by the cluster scheduler to place your workload on the best suiting server node.'
type: complex
required: false
group: resources
patch: resourceRequests.yaml
subquestions:
- variable: cpu
label: CPU
description: 'Indicates the average CPU usage of the application. 1000 CPU shares = 1 CPU core'
type: int
default: 500
range:
min: 100
max: 8000
step: 100
unit: 'm'
readableUnit: 'shares'
validation:
- type: minRatio
value: '1'
variable: limits.memory
description: "Memory requests must be equal to memory limits. We don't allow memory over-commit in our cluster to prevent out of memory errors. Please adjust your request or limit."
- type: maxRatio
value: '1'
variable: limits.memory
description: 'Memory requests can not be higher than memory limits. Please adjust your request or limit.'
More about Gimlet
Gimlet is the Kubernetes Application Manager that helps developers and platform teams on the first day, any day.
Besides easing configuration management, providing deployment tooling, it also focuses on developer onboarding and application operations concerns.
Check out Gimlet on https://gimlet.io



