A 6.37 EUR a month single node Kubernetes cluster on Hetzner with vitobotta/hetzner-k3s

Laszlo Fogas

I did a live stream recently, trying out Vito Botta's hetzner-k3s tool (vitobotta/hetzner-k3s) where I wanted to provision a single node Kubernetes cluster on Hetzner.
My first impressions were promising: Vito's tool was polished and Hetzner was much faster than most clouds I used. The tool created a 2 core/4GB/6.37EUR a month node and installed the cluster in a minute, and the tear down was not more than 15 seconds. I could rapidly iterate with my config and stay in the flow.
This blog post is a follow up to the stream, sharing my config for
- starting up a single node cluster,
- installing Nginx as an ingress controller,
- and exposing it on port 80 and 443 to the world.
Why kubernetes on a VPS you may ask
Kubernetes is creeping into our lives by becoming the deployment standard at companies. While mongering complexity is a common side effect of adopting the platform, it does not have to be like that. Most Kubernetes commands are not more complex or risky than copying a sudo command from the Digital Ocean blog to a VPS
The resource overhead of the presented setup is also surprisingly low. Only five pods running in the cluster utilizing 10% of the CPU and 3 percent of the RAM.
$ kubectl describe node stream-cx21-master1
...
Allocatable:
cpu: 2
memory: 3919824Ki
...
Non-terminated Pods: (5 in total)
Name CPU Requests CPU Limits Memory Requests Memory Limits Age
---- ------------ ---------- --------------- ------------- ---
coredns-59b4f5bbd5-45cx9 100m (5%) 0 (0%) 70Mi (1%) 170Mi (4%) 5m10s
hcloud-cloud-controller-manager-574ff96c5c-bk4zn 100m (5%) 0 (0%) 50Mi (1%) 0 (0%) 5m10s
hcloud-csi-controller-79796587c7-vt4n5 0 (0%) 0 (0%) 0 (0%) 0 (0%) 5m10s
hcloud-csi-node-bv57b 0 (0%) 0 (0%) 0 (0%) 0 (0%) 5m10s
system-upgrade-controller-cb858644f-rp6q7 0 (0%) 0 (0%) 0 (0%) 0 (0%) 5m10s
...
Allocated resources:
Resource Requests Limits
-------- -------- ------
cpu 200m (10%) 0 (0%)
memory 120Mi (3%) 170Mi (4%)
Prerequisites
Install hetzner-k3s
Follow the instructions on https://github.com/vitobotta/hetzner-k3s#installation
Get a Hetzner API key
You need to create a project on the Hetzner cloud console, and then an API token with both read and write permissions (sidebar > Security > API Tokens); you will see the token only once, so be sure to take note of it.
Make the token available in your terminal now for later use:
export HCLOUD_TOKEN=g0cY....
Install kubectl and helm
Cluster configuration
vitobotta/hetzner-k3s is a single binary that creates everything that is needed for a kubernetes cluster on Hetzner. Think networks, load balancers, firewalls and VMs.
It takes a yaml configuration file parameter. Use this yaml for creating the cluster:
---
cluster_name: tutorial
kubeconfig_path: "./kubeconfig"
k3s_version: v1.26.4+k3s1
public_ssh_key_path: "~/.ssh/id_ed25519.pub" ## <-- replace with your SSH public key path
private_ssh_key_path: "~/.ssh/id_ed25519" ## <-- replace with your SSH private key path
use_ssh_agent: true
ssh_allowed_networks:
- 78.92.157.253/32 ## <-- replace with your IP
api_allowed_networks:
- 78.92.157.253/32 ## <-- replace with your IP
private_network_subnet: 10.1.0.0/16
schedule_workloads_on_masters: true
masters_pool:
instance_type: cx21
instance_count: 1
location: hel1
worker_node_pools:
additional_packages:
- haproxy
post_create_commands: ## Downloads an HAProxy configuration file for port 80/443
- curl -o /etc/haproxy/haproxy.cfg https://gist.githubusercontent.com/laszlocph/61642778fb61e3d7c1766d31e676c0f7/raw/bf836c73ce24b07b2423251316e6f030ada6b3c9/haproxy.cfg
- service haproxy reload
Create the cluster now with:
hetzner-k3s create --config tutorial.yaml
Validating configuration......configuration seems valid.
=== Creating infrastructure resources ===
Creating network...done.
Creating firewall...done.
SSH key already exists, skipping.
Creating placement group stream-masters...done.
Creating server stream-cx21-master1...
...server stream-cx21-master1 created.
Waiting for successful ssh connectivity with server stream-cx21-master1...
...server stream-cx21-master1 is now up.
=== Setting up Kubernetes ===
Deploying k3s to first master stream-cx21-master1...
[INFO] Using v1.26.4+k3s1 as release
[INFO] Downloading hash https://github.com/k3s-io/k3s/releases/download/v1.26.4+k3s1/sha256sum-amd64.txt
[INFO] Downloading binary https://github.com/k3s-io/k3s/releases/download/v1.26.4+k3s1/k3s
[INFO] Verifying binary download
[INFO] Installing k3s to /usr/local/bin/k3s
[INFO] Skipping installation of SELinux RPM
[INFO] Creating /usr/local/bin/kubectl symlink to k3s
[INFO] Creating /usr/local/bin/crictl symlink to k3s
[INFO] Creating /usr/local/bin/ctr symlink to k3s
[INFO] Creating killall script /usr/local/bin/k3s-killall.sh
[INFO] Creating uninstall script /usr/local/bin/k3s-uninstall.sh
[INFO] env: Creating environment file /etc/systemd/system/k3s.service.env
[INFO] systemd: Creating service file /etc/systemd/system/k3s.service
[INFO] systemd: Enabling k3s unit
[INFO] systemd: Starting k3s
Waiting for the control plane to be ready...
Saving the kubeconfig file to /home/laszlo/projects/hetzner-stream/kubeconfig...
...k3s has been deployed to first master stream-cx21-master1 and the control plane is up.
=== Deploying Hetzner drivers ===
...Cloud Controller Manager deployed
...CSI Driver deployed
...k3s System Upgrade Controller deployed.
Verify the cluster with:
$ export KUBECONFIG=kubeconfig
$ kubectl get nodes
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION
stream-cx21-master1 Ready control-plane,etcd,master 3m13s v1.26.4+k3s1
Install Nginx
helm repo add ingress-nginx https://kubernetes.github.io/ingress-nginx
helm install ingress-nginx ingress-nginx/ingress-nginx \
--set controller.service.type=NodePort \
--set controller.service.nodePorts.http=32080 \
--set controller.service.nodePorts.https=32443
Validate the installation:
$ kubectl get pods,svc
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pod/ingress-nginx-controller-5ff6bb675f-mrcrn 1/1 Running 0 35s
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
service/ingress-nginx-controller NodePort 10.43.93.39 <none> 80:32080/TCP,443:32443/TCP 35s
service/ingress-nginx-controller-admission ClusterIP 10.43.75.218 <none> 443/TCP 35s
service/kubernetes ClusterIP 10.43.0.1 <none> 443/TCP 21m
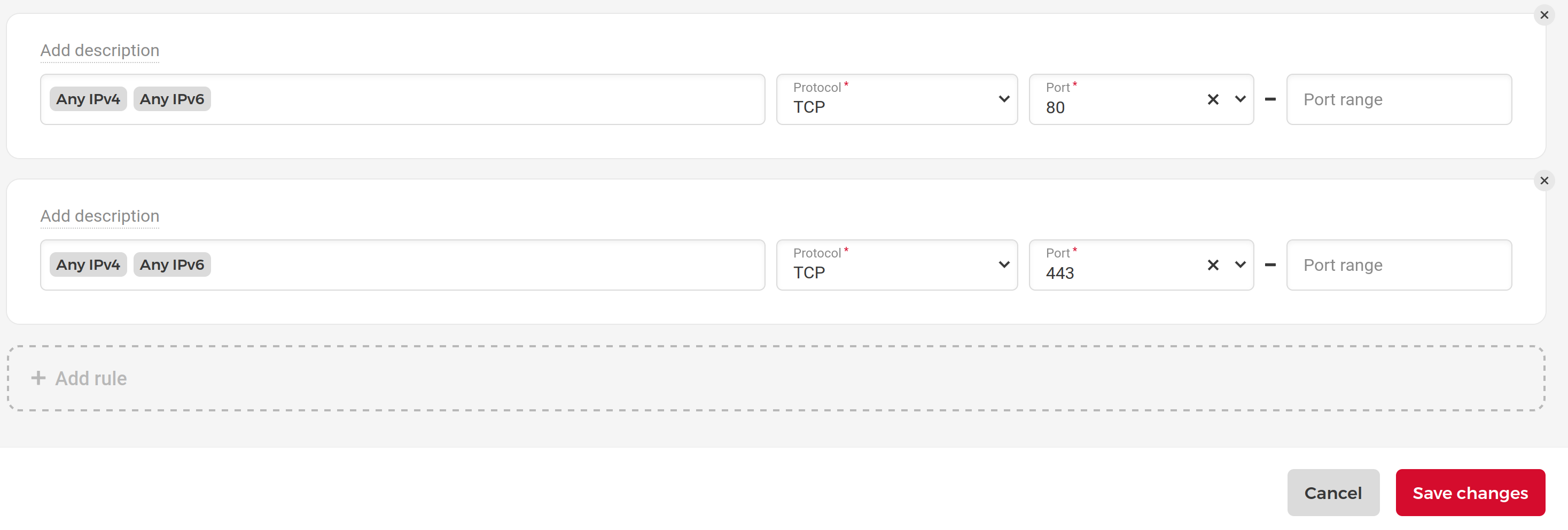
Open port 80 and 443 on the Hetzner firewall
sidebar > Firewalls > tutorial > Add rule
Then validate if you see the Nginx 404 page:
$ curl http://37.27.3.154/
<html>
<head><title>404 Not Found</title></head>
<body>
<center><h1>404 Not Found</h1></center>
<hr><center>nginx</center>
</body>
</html>
Optionally you can set a DNS entry that points to your server's IP address.
Deploy a static website
To test the ingress controller we are going to use the nip.io dynamic DNS service, and the onechart/static-site helm chart. This helm chart pulls the source code from git, builds it, then serves the files of a static website.
helm repo add onechart https://chart.onechart.dev
helm install my-react-app onechart/static-site \
--set gitCloneUrl=https://github.com/gimlet-io/reactjs-test-app.git \
--set buildImage=node:16.20-buster \
--set buildScript="npm install && npm run build" \
--set builtAssets=build/ \
\
--set ingress.host=my-react-app.37.27.3.154.nip.io \
--set ingress.annotations.'kubernetes\.io/ingress\.class'=nginx
Validate the deployment:
$ kubectl get pods,ing
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pod/ingress-nginx-controller-5ff6bb675f-mrcrn 1/1 Running 0 32m
pod/my-react-app-57966d7dfd-5vltr 0/1 Init:0/1 0 11s
NAME CLASS HOSTS ADDRESS PORTS AGE
ingress.networking.k8s.io/my-react-app <none> my-react-app.37.27.3.154.nip.io 80 11s
(you can track the build progress with: kubectl logs -f deploy/my-react-app -c init-con)
And access the application:
curl http://my-react-app.37.27.3.154.nip.io/
Cleanup
You can clean up your experiment with:
hetzner-k3s delete --config tutorial.yaml
Onwards!



